Estimated reading time: 4 minutes
In recent years data analytics and the importance of data analysis has gone up significantly.
As a result of this, the quantities of data now been processed has increased.
Here in Data Analytics Ireland, we will look to explain the concept, please share or link to this article so others can see its contents.
To begin with, the reason for this is that the digital economy has taken off, in particular:
(A) Automation of tasks has become easier.
(B) Less use of paper, becoming a greener economy.
(C) Technology improvements have meant that storage and big data processing make the process of delivering services easier.
(D) Career opportunities for professionals with good skills have increased.
(E) A wide range of open source and paid tools are now easily available that help to process and report on the data.
(F) Entry requirements are easy, and this coupled with an ability to quickly acquire knowledge and skills helps entry whether you want to be full time or part-time.
(G)Knowledge and skills have improved as access to online learning has improved significantly.
As a result of all this:
(A) Large data volumes need to be analysed.
(B) Consumers’ habits about how they use a service or the information they look for now has a digital footprint.
(C) Now once a consumer has used a service ( whether purchased or not), the ability to understand their habits can be captured to deliver as follows:
- The services they want.
- The products they want.
- Quicker turnaround time.
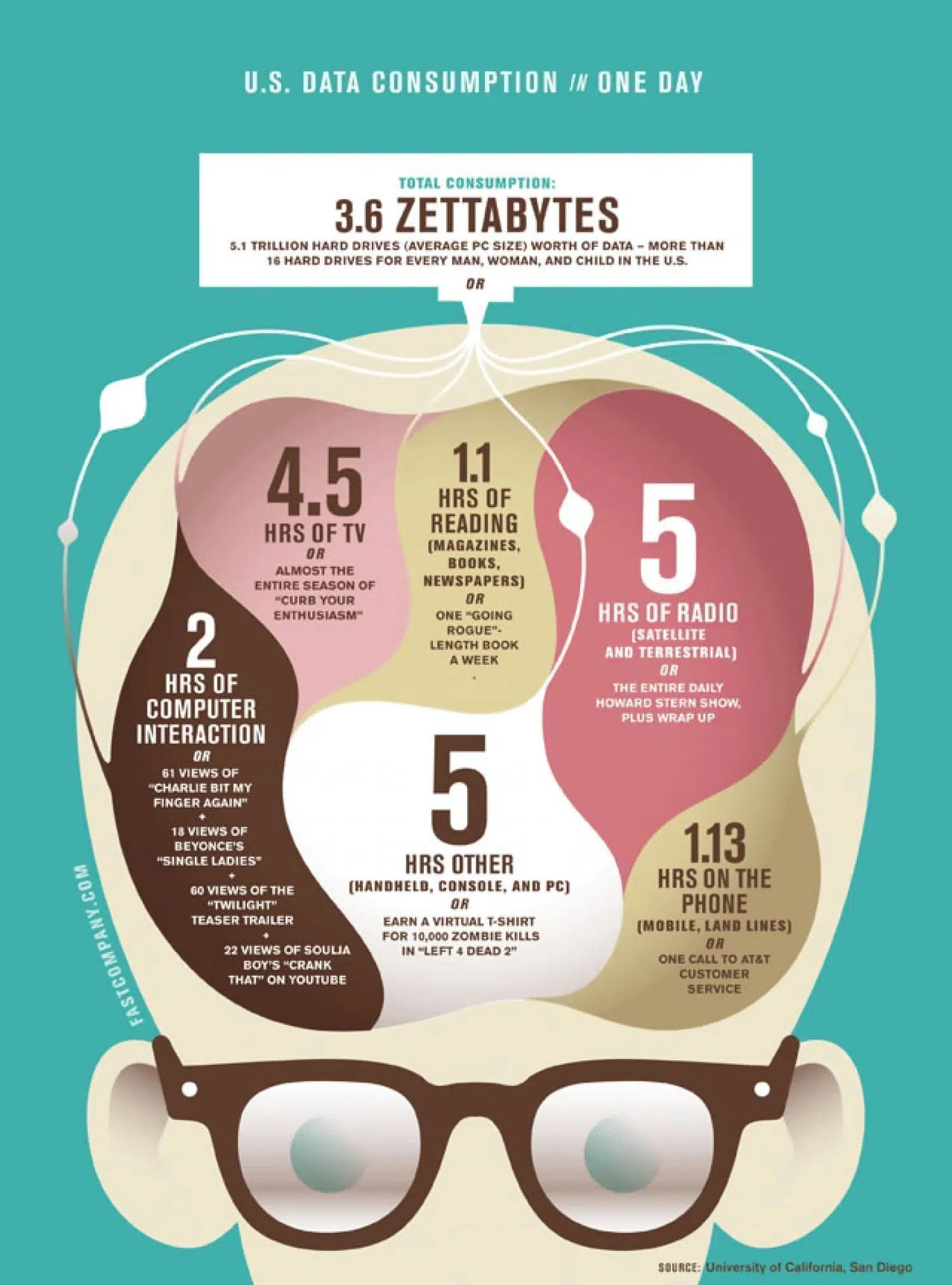
How can this help with all the data that is captured and stored?
So in this article, we have already outlined what the background is as to how the industry has evolved to where data analytics is now.
As outlined, all information traditionally would not have been stored in a format that was easily accessible.
Step 1 – Data Capture
To understand what you want to analyse, and help draw conclusions accurately, a data analyst will work with their technical colleagues to ensure that the correct data is captured.
Data capture of raw data, can happen in a number of ways:
- User input.
- Interaction with a website or application.
- Consuming a service.
- Requesting a service be completed.
- Social media interaction.
- In a lot of cases now this happening in real time.
Once the completeness and accuracy are fulfilled, your data quality will become less of an issue, the more you use data profiling.
Have a look here for further information on completeness and what is data profiling and its benefits.
Step 2 – Analysing
(A) You create visual charts of it; this allows the viewer of the information to get an initial view of the information without looking at the underlying data. Sometimes this will show patterns in data or clusters or the types of data you capture.
(B) Using data science statistics to see if they can explain the data. This could show information such as how data is correlated or otherwise. Also, probabilities could be calculated to show what outcomes might happen in the future.
(C) Data analysts might also need to understand how to build a machine learning model to use complex algorithms, to explain the data better, sometimes patterns that are not immediately understood can be unearthed and investigated further.
- There are two approaches commonly used for this, namely supervised and unsupervised machine learning.
Step 3 – Presenting
An emphatic NO is an answer, but this is where some of the visualisation tools come in!
Visually presenting data points, very quickly allows a viewer of the information to come to a decision quickly, and the tools that are outlined below will help with that process.
These are a handful that will allow the data to be sliced and diced, there are many more out there, but they all allow data to be drilled down into and get to a real understanding what is going on.
Some of the tools include Tableau, Power BI, and Python( it has libraries that do a nice job)
Step 4 – Decision Making
So after all this analysing, there needs to be decisions made:
(A) Do you have the data in order and in the correct format?
(B) In a place that it can be accessed and reviewed.
(C) Relevant to when the decision needs to be made.
From the outset, as part of the work of performing the data analytics, an assessment needs to be made as to how often a decision will need to be made, with what data, and when.
At this point, the decision-makers should have a set of data ready for them to look over and reliably make a decision
Based on the data returned, if they can’t make a decision then possibly, steps 1-3 should be reviewed and revisited.
Often what happens, is what information that was required to make a change needs to be updated, or improved upon.
It is the job of the teams that manage the data sets to source that data and or change how they present it, to now reflect the decision that needs to be made.
