Estimated reading time: 4 minutes
Often you will hear about deleting table records with SQL, but how is this achieved, if you have not done it before?
In previous videos on SQL we discussed how to update records in SQL , how to insert data into a table in SQL.
You could be faced with the scenario where there is data that you no longer need, as a result, it needs to be deleted.
So lets work through three different scenarios as follows:
(A) Delete a record based on a unique identifier, in this instance CUSTOMER_NO.
(B)Delete multiple customer records at once using CUSTOMER_NO as the column that will identify the records.
(C) Delete a record where it equals a particular column value.
Our initial dataset will look like this:
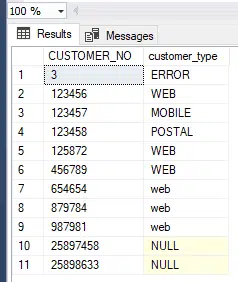
Delete a record based on a unique identifier
DELETE FROM dbo.CUSTOMER WHERE CUSTOMER_NO = 987981 select * from dbo.CUSTOMER
When the above code is run it gives the following output.
As can be seen it now has ten records and the row for CUSTOMER_NO = 987981 has been removed.
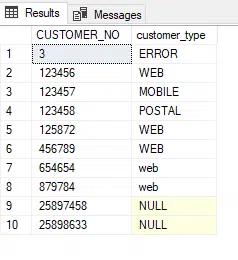
Delete multiple customer records at once
In the above scenario we have deleted just one record, but most likely you will want to remove more than one.
This code below will complete this at once. Remember the column we are using is a primary key column, hence all the values are unique.
It may be the case that you are doing to have to do this on a column that does not have unique values, the code will still work.
I would caution though that using the primary key column value always allows you to only remove the ones that are not needed.
It could be the case that there are genuine values that need to remain, even if they are duplicated.
DELETE FROM dbo.CUSTOMER WHERE CUSTOMER_NO in(3,25897458,25898633) select * from dbo.CUSTOMER
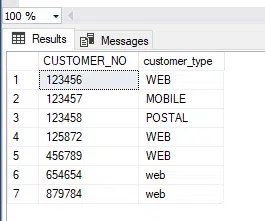
As can be seen running the above code now leaves us with seven rows, down from ten and the three rows we had in the SQL have been removed.
Deleting a record where it equals a particular column value
So our final scenario is where we need to find a particular value in a column , and it is exists , then delete the whole record for that row.
Here we are not relying on the primary key, but basically a string search in the customer_type column.
When this SQL is run, it supposed remove two rows and leave us with five records.
The problem that you will encounter
There will be a problem with this as the primary key , even though is not been referenced will throw an error.
The error in this instance relates to the the CUSTOMER_NO on the table customer
- It has a foreign key equivalent column in the sales table.
In essence you cant leave out the primary key value when completing this SQL statement.
As a result both tables need to be updated, where the primary key value exists.
DELETE FROM dbo.CUSTOMER WHERE customer_type = 'POSTAL' select * from dbo.CUSTOMER ** the above code will fail with the below error: The DELETE statement conflicted with the REFERENCE constraint "FK__SALES__CUSTOMER___267ABA7A". The conflict occurred in database "SALES", table "dbo.SALES", column 'CUSTOMER_NO'. The statement has been terminated.
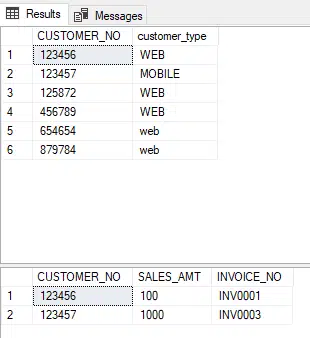
Our table in sales looks like this:
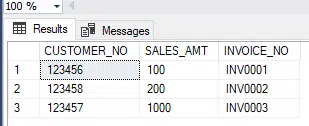
Updating our logic as follows:
DELETE FROM dbo.SALES where SALES.CUSTOMER_NO = 123458 ---> This line needs to be run first as the next line checks if this exists as a foreign key. DELETE FROM dbo.CUSTOMER where CUSTOMER.CUSTOMER_NO = 123458 and customer_type = 'POSTAL' select * from dbo.CUSTOMER select * from dbo.SALES
Results in:
To summarise there are a number of things to consider:
- It is important to always check if there is a primary and foreign key relationship.
- Specifically not checking these relations will result in the SQL outputting an error.
- Under these circumstances a review of all tables before proceeding is advised.
- Ensure you have your tables backed up before doing any deletions!
