Estimated reading time: 3 minutes
Python arrays are used to manage how data is analyzed and have the data in a structured form for the data analyst or data scientist to use.
What is an Array?
An array has the following properties:
- The data in it is of the same data type.
- The data is stored as contiguous memory locations, meaning the lowest value is at index 0 and the last value is at the highest index value.
- Arrays assign index values to each data point contained within it.
- You can append values to the array.
- You can delete values from the array, that is it is mutable.
What are the differences between arrays and lists?
For the most part arrays and lists are the same, but with one difference:
A list can store any data type you want e.g. strings, integers, etc.
On the other hand, arrays can only store data that is of the same data type.
What are the different ways that I can create an array?
(A) Use Numpy
# Use numpy
import numpy as np
a = np.array([1,2,3,4])
print(a)
print(type(a))
print(a.dtype)
Output:
[1 2 3 4]
<class 'numpy.ndarray'>
int32
If we have one of the values as a string, all the other values are converted to a string , as follows:
# Use numpy
import numpy as np
a = np.array([1,2,3,'4'])
print(a)
print(type(a))
print(a.dtype)
Output:
['1' '2' '3' '4']
<class 'numpy.ndarray'>
<U11
# <U11 - When this happens, it means one of the values was returning as a string
# All the other values in the array as a result are converted to strings
(B) Use an array
import array as test_array
a = test_array.array('i',[1,2,3])
print(a)
print(type(a))
Output:
array('i', [1, 2, 3])
<class 'array.array'>
On the Python.org website, below is the list of values that can be populated into the above program, depending on what your need is:
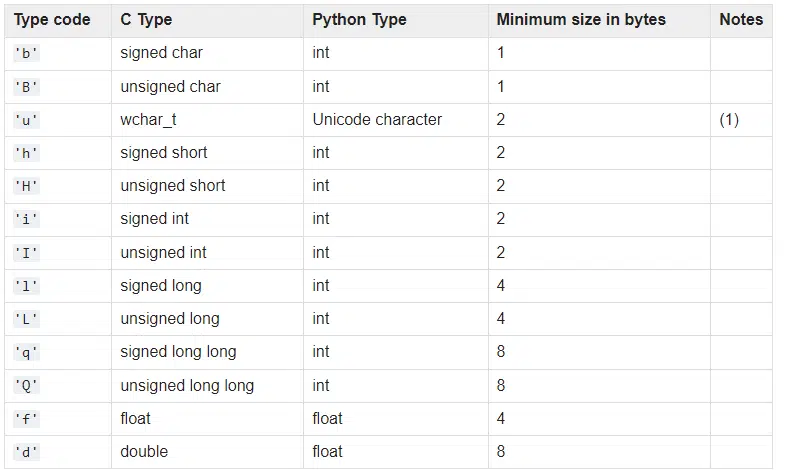
When should I use arrays?
It really depends on the nature of your python program, but below are some examples that may help you make a decision:
(A) Many variables of the same type: There may be a scenario where you have to create an array to store data that is of the same data type. For example, you have a list of codes to look up against, which are all integers.
(B) Faster and more efficient: If speed is what you are looking for using arrays, will help improve the performance of your computer program, using lists is much slower.
(C) Compactability and efficiency: If the nature of your program needs to store large amounts of data that needs to be accessed quickly, then this would be a good reason to use them.
(D) Ability to retrieve data quickly through indexing: As arrays have index values associated with them, the data can be easily retrieved.
(E) Need to compute some mathematical values: Arrays are excellent for any numerical operations you need to complete, as the level of coding is minimal.
import array as test_array
a = test_array.array('i',[1,2,3])
mydivider = 2
mynewlist = [x / mydivider for x in a]
print(mynewlist)
result:
[0.5, 1.0, 1.5]So in summary:
Speed, efficiency, and ease of use are the main reasons to use an array.
We use arrays here how to show percentage differences between files in python why not go over and see it in action!
